本文介绍提出以及改进 Multi-Task Deep Neural Networks (MT-DNN) 的两篇论文 Multi-Task Deep Neural Networks for Natural Language Understanding 和 Improving Multi-Task Deep Neural Networks via Knowledge Distillation for Natural Language Understanding。第一篇论文提出了多任务模型MT-DNN,该模型是基于Transformer Encoder 的BERT模型,该模型将多任务学习和语言模型预训练结合起来,用于语言表达学习。第二篇论文使用知识蒸馏技术对MT-NDD模型进行了改进。
多任务学习 Multi-Task Learning (MTL) 不仅利用了大量的跨任务数据,而且还受益于正则化效应,这种效应导致更一般的表示,以适应新的任务和域。尽管集成学习可以提高模型性能,但是使用诸如MT-DNN的大型DNN的集合来工作可能非常昂贵。所以使用知识蒸馏技术确保模型效果的同时(单模型效果与集成模型效果相当)减小模型大小(参数量)。
Multi-Task Deep Neural Networks for Natural Language Understanding
Abstract
In this paper, we present a Multi-Task Deep Neural Network (MT-DNN) for learning representations across multiple natural language understanding (NLU) tasks. MT-DNN not only leverages large amounts of cross-task data, but also benefits from a regularization effect that leads to more general representations in order to adapt to new tasks and domains. MT-DNN extends the model proposed in Liu et al. (2015) by incorporating a pre-trained bidirectional transformer language model, known as BERT (Devlin et al., 2018). MT-DNN obtains new state-of-the-art results on ten NLU tasks, including SNLI, SciTail, and eight out of nine GLUE tasks, pushing the GLUE benchmark to 82.7% (2.2% absolute improvement). We also demonstrate using the SNLI and SciTail datasets that the representations learned by MT-DNN allow domain adaptation with substantially fewer in-domain labels than the pre-trained BERT representations. The code and pre-trained models are publicly available at this https URL.
摘要
在本文中,我们提出了一个多任务深度神经网络(MT-DNN),用于跨多种自然语言理解(NLU)任务的学习表示。 MT-DNN不仅利用了大量的跨任务数据,而且还利用正则化效应带来的好处,从而产生更一般的表示,以帮助适应新的任务和领域。 MT-DNN扩展了Liu等人(2015)提出通过结合预先训练的双向Transformer语言模型,称为BERT(Devlin等,2018)。 MT-DNN在10个NLU任务中获得了最新的结果,包括SNLI,SciTail和9个GLUE任务中的8个,将GLUE基准推至82.7%(绝对改进2.2%)。我们还展示了在SNLI和SciTail数据集上,MT-DNN学习的表示允许域自适应,其域内标签比预训练的BERT表示少得多。代码和预先训练的模型可在https://github.com/namisan/mt-dnn上公开获取。
MT-DNN模型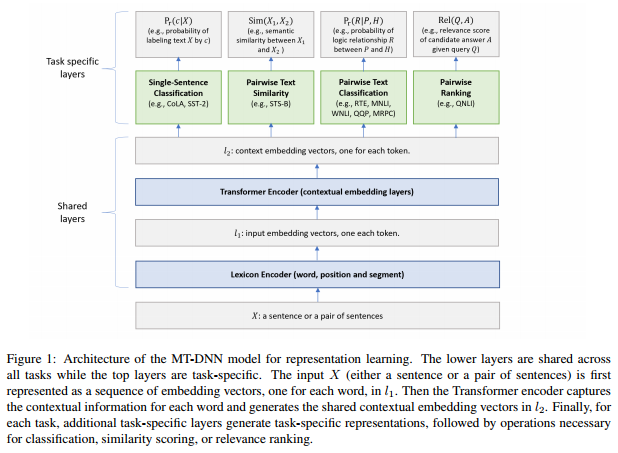
MT-DNN模型的训练算法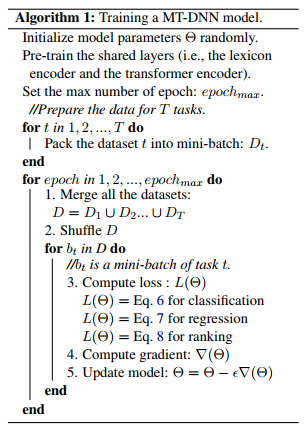
Improving Multi-Task Deep Neural Networks via Knowledge Distillation for Natural Language Understanding
Abstract
This paper explores the use of knowledge distillation to improve a Multi-Task Deep Neural Network (MT-DNN) (Liu et al., 2019) for learning text representations across multiple natural language understanding tasks. Although ensemble learning can improve model performance, serving an ensemble of large DNNs such as MT-DNN can be prohibitively expensive. Here we apply the knowledge distillation method (Hinton et al., 2015) in the multi-task learning setting. For each task, we train an ensemble of different MT-DNNs (teacher) that outperforms any single model, and then train a single MT-DNN (student) via multi-task learning to distill knowledge from these ensemble teachers. We show that the distilled MT-DNN significantly outperforms the original MT-DNN on 7 out of 9 GLUE tasks, pushing the GLUE benchmark (single model) to 83.7\% (1.5\% absolute improvement\footnote{ Based on the GLUE leaderboard at this https URL as of April 1, 2019.}). The code and pre-trained models will be made publicly available at this https URL.
摘要
本文探讨了利用知识蒸馏改进多任务深度神经网络(MT-DNN)(Liu et al。,2019)来学习跨多种自然语言理解任务的文本表示。尽管集成学习可以提高模型性能,但是服务于诸如MT-DNN的大型DNN的集合可能非常昂贵。在这里,我们将知识蒸馏方法(Hinton等,2015)应用于多任务学习环境中。对于每项任务,我们培训不同MT-DNN(教师)的集合,其优于任何单一模型,然后通过多任务学习训练单个MT-DNN(学生)以从这些集合教师中提取知识。我们表明,蒸馏的MT-DNN在9个GLUE任务中的7个中明显优于原始MT-DNN,将GLUE基准(单个模型)推至83.7%(1.5%绝对改进\脚注{基于GLUE排行榜这个https网址截至2019年4月1日。})。代码和预先训练的模型将在此https URL https://github.com/namisan/mt-dnn 公开发布。
MT-DNN模型的训练算法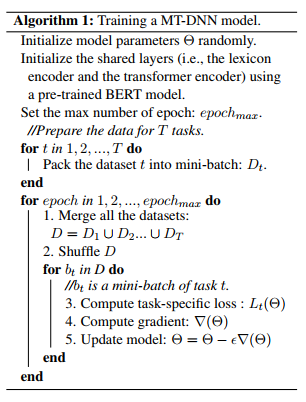
MT-DNN知识蒸馏过程

